Barbervax may be used in all classes of sheep: lambs, hoggets, ewes and rams. Previously unvaccinated animals are primed after 3 doses which should be administered before the main Barber’s pole risk period – normally January to April. 6-weekly vaccination boosts are required to maintain protection over the Barber’s pole season. Vaccine should be stored in the fridge (2-8˚C) and transported in a portable cool box with ice bricks. Keep the vaccine cool during administration – keep in the shade and place in a can cooler, or wrap in a damp towel.
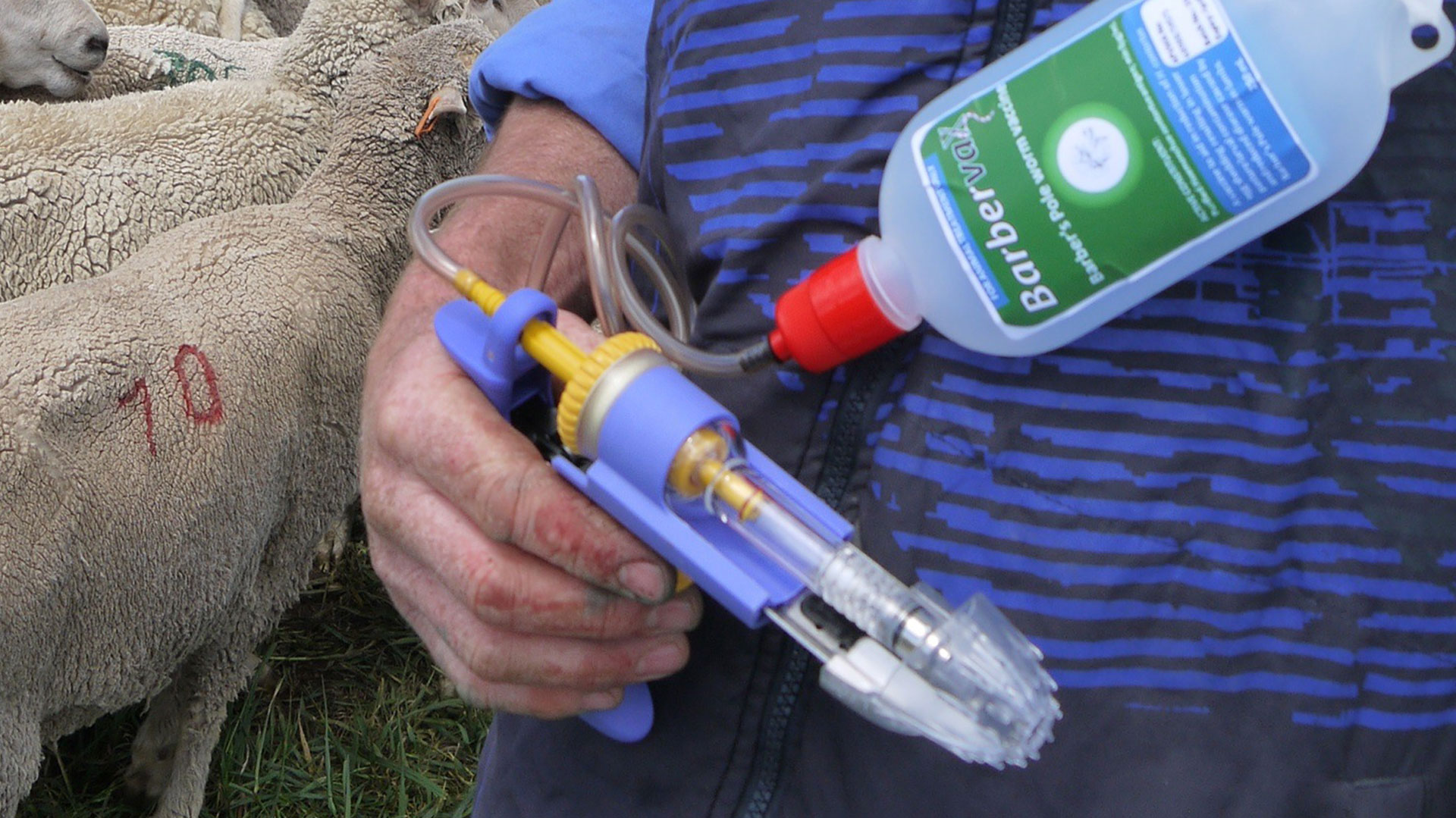
A standard 1ml dose given under the skin to all animals, irrespective of body weight. If a different vaccine (e.g. 5 in 1) is being given at the same time, it should be administered at a different site e.g. on the opposite side of the neck. Barbervax is not a knockdown product, it controls disease caused by Barber’s pole worm by reducing worm egg counts and preventing build-up of infection.
Drenches may still be required before immunity develops, or to treat for other worms – please refer to your regional WormBoss worm control program and Drench Decision Guide
The vaccine is given as a 1ml dose under the skin. All sheep should receive 1ml, irrespective of body weight. To ensure accuracy, it is better to use a 1ml fixed volume vaccinator, rather than an adjustable dose model. Behind the ear is a popular injection site. If a different vaccine (e.g. 5 in 1) is being given at the same time, it should be given at a different site e.g. on the opposite side of the neck. As with all vaccines self-injection of Barbervax could be painful. A one-handed ‘safety’ vaccinator is recommended to reduce the hazard.

All schedules should be followed accurately: do not extend the gaps between vaccination
How to buy Barbervax
Visit our ‘Buy’ page to learn how you can order Barbervax, no matter where you are in the world.
Specific instructions
How to use in lambs or hoggets
The tables below tell you how to use Barbervax in lambs or hoggets which have not previously been vaccinated. Sheep (e.g. ewes, hoggets) which have received a course of vaccine during their first season and will be retained, need only receive 4 vaccinations, 6 weeks apart over their second and any subsequent seasons. This course of vaccine should ideally start two weeks before barber’s pole worm is expected to appear.
Vaccination no. | When to adminster | Considerations |
V1 | At lamb marking | |
V2 | 3-4 weeks after marking | Generally administered at weaning. This should be given with an effective drench to control scour worms as well as any early barbers pole worm. Lambs should be moved to a prepared low worm-risk paddock, ideally where sheep have not grazed for 3 months |
V3 | 3-4 weeks after V2 | |
V4 | 6 weeks after V3 | |
V5 | 6 weeks after V4 | |
V6 | 6 weeks after V5 | V6 may only be required if May is mild and wet. |
To avoid a special muster of ewes with lambs at foot, some may prefer to delay marking by a week and to wean a week earlier. That way, V2 can be given at weaning and V3 to the newly weaned sheep 3-4 weeks later. | ||
How to use in breeding ewes
Using Barbervax in breeding ewes not previously vaccinated.
Vaccination no. | When to adminster | Considerations |
V1 | 8-9 weeks pre-lambing | |
V2 | 4-5 weeks pre-lambing | |
V3 | 1-2 weeks pre-lambing | This should be given with an effective pre-lambing drench to control scour worms as well as any early barbers pole worm and the ewes should be moved to a low worm-risk lambing paddock that has been prepared over the previous 6 months. |
V4 | At lamb marking | |
V5 | 6 weeks intervals after V4 | Continue while protection is required. |